Prostatitis comes in two forms - acute and chronic. If acute inflammation is quickly treated with antibiotics, chronic prostatitis becomes a serious problem in older men, negatively affecting quality of life. Chronic prostatitis can be caused by both infection and congestion in the pelvic organs. The disease requires long-term and complex treatment.
Classification of the disease
Chronic prostatitis in men is divided into two types - congestive (abacterial, congestive) and infectious.
Chronic congestive prostatitis is a consequence of impaired trophism of the prostate. The disease develops with heart failure or lack of regular sex life.
Chronic abacterial prostatitis is characterized by moderate symptoms and the absence of acute pain syndrome. When analyzed, no infectious agents are detected in the secretion of the prostate, therefore the disease is called abacterial.
Infectious chronic prostatitis is a consequence of untreated bacterial inflammation. The disease begins with an acute form due to infection of the prostate gland. The disease becomes chronic due to the lack of adequate and timely therapy. Chronic infectious prostatitis is characterized by periodic exacerbations.
Causes of chronic non-infectious prostatitis
Speaking of chronic prostatitis, most often we mean a non-infectious disease triggered by congestion in the pelvic organs. This is due to a violation of the trophism of the prostate - blood circulation, lymph flow, outflow of prostate secretions.
This form of the disease is directly related to lifestyle and is considered a disease of office workers. The main reason for the development of congestive prostatitis is physical inactivity.
Among the factors predisposing to the development of congestive prostatitis, there are:

- sedentary work;
- lack of regular sports;
- unbalanced diet;
- obesity;
- bad habits;
- varicose veins;
- hemorrhoids;
- irregular sex life.
The disease develops against the background of any conditions, accompanied by circulatory disorders of the lower extremities. Quite often, prostatitis appears with obesity, when, as a result of an increased load on the lumbar region and lower limbs, metabolic processes in this zone are disrupted.
If due to the peculiarities of the profession you have to sit all day, you need to move at least in the evening.
Bad habits can trigger the development of prostatitis. Smoking destroys blood vessels and disrupts normal blood flow. Due to the physiological characteristics of a person, this primarily affects the blood circulation of the lower extremities and the pelvic region.
Sex plays an important role in the functioning of the prostate gland. The optimal number of intercourse per week for a man over 40 years old is 3-4. A smaller amount leads to a violation of the outflow of prostate secretion, a larger amount leads to organ depletion.
Another cause of congestive prostatitis is heart failure. This disease is characterized by impaired blood circulation, including in the pelvic organs.
The reasons for the development of chronic infectious prostatitis
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is a consequence of untreated acute inflammation of the prostate gland. This form of the disease is characterized by severe symptoms and the presence of pathogenic agents found in the secretion of the prostate.
The most common causative agents of infectious prostatitis:
- E. coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- staphylococcus and streptococcus;
- chlamydia;
- ureaplasma;
- Trichomonas;
- fungal flora.
The infection enters the prostate gland in three ways: with the blood flow, lymph, or through the urethra. The last path of penetration of pathogenic agents is valid in cases of infection with chlamydia, ureplasma or Trichomonas.
Reasons for the development of the disease:
- decreased immunity;
- severe hypothermia;
- stress;
- long-term antibiotic therapy.
Conditionally pathogenic bacteria are always present in the body, and only strong immunity does not allow them to activate.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis develops from an acute form in the following cases:
- the presence of a chronic focus of infection;
- incorrectly selected antibiotic therapy;
- late discontinuation of treatment;
- weakened immunity.
In most cases, the chronic form of the disease develops precisely because of improper treatment. This happens when the scheme of antibiotic therapy is not correctly drawn up or self-medication. Stopping antibiotics when you feel better results in the disease agent not being completely destroyed. Any decrease in immunity or hypothermia in this case leads to the re-development of the disease.
The most difficult to treat is fungal prostatitis caused by yeast-like fungi. This pathogen quickly develops resistance to antifungal drugs, which makes treatment more difficult and increases the risk of developing a chronic form of the disease.
Symptoms of the disease
In chronic prostatitis, symptoms are mild, however, with a decrease in immunity or after stress, the disease worsens.
The most common symptoms of chronic prostatitis in men are:
- urination disorder;
- heaviness in the prostate;
- weakening of potency;
- night urge to use the toilet.
With exacerbation of chronic prostatitis, pain in the bladder and perineum is noted. The frequency of urging to the toilet can reach 10 per hour. At the same time, the urine stream is weak, it is necessary to strain the muscles to urinate, but the process itself does not bring relief, and repeated urges appear after a few minutes.
The symptoms and treatment of chronic prostatitis largely depend on the form of inflammation. With congestive prostatitis, erection problems are common. This is due to impaired blood circulation. Ejaculation can occur quickly, or absent altogether due to thickening of the prostate secretion.
In case of infectious inflammation of the prostate gland or chronic bacterial prostatitis, pain during urination and burning in the urethra after ejaculation may occur. Such symptoms are accompanied by irritation of the urethral mucosa by disease-causing agents contained in the secretion of the prostate.
Prostatitis and erectile dysfunction

Inflammation of the prostate is not visible to the eye, the symptoms of chronic prostatitis have no visible manifestation, but refer to internal disorders. One of the characteristic symptoms of the disease is a weakening of erection.
Erectile dysfunction in congestive prostatitis develops in several stages. The disease itself can proceed for a long time without severe symptoms, and signs of prostatitis will appear only with a strong weakening of the immune system.
Abacterial inflammation of the prostate can be suspected by changes in erection. At the beginning of the development of the disease, an increase in potency is noted. The man is quickly aroused, but ejaculation also comes quickly. This is due to a change in the viscosity of the secretion of the prostate gland. Discomfort may be felt during ejaculation, but pain is characteristic of infectious but not congestive prostatitis.
This causes a number of psychological problems that aggravate the course of the disease. Erectile dysfunction due to problems with blood flow is aggravated by fear of a sexual partner, which can lead to the development of impotence against the background of prostatitis.
Urinary Disorder
Problems with urodynamics are observed in all forms of prostatitis.
Chronic abacterial inflammation is characterized by nocturnal urge to urinate. It is caused by swelling of the prostate gland, which is aggravated at night. There is a weakening of urine pressure and the need to tighten the muscles of the pelvic floor to urinate. At the same time, he feels heaviness and fullness in the bladder, and occasional spasms may appear. Due to the frequent urge to use the toilet at night, sleep problems and insomnia appear. All this affects the psychological state of the man and further aggravates the course of the disease, since against the background of stress there is a decrease in immunity and a slowdown in metabolic processes.
Men often complain of cramps in the lower abdomen, which is explained by the increased tone of the muscles of the bladder. Usually, severe symptoms of prostatitis are noted with a decrease in immunity. Without an exacerbation of the disease, pain syndrome may be completely absent.
Congestive prostatitis is characterized by severe prostate edema. The contours of the organ become indistinct, the prostate itself swells and increases in size. In this case, there may be a feeling of fullness in the rectum and increased discomfort during bowel movements. Problems with urination are due to compression of the urethra by a swollen prostate gland.
Why is prostatitis dangerous?

The consequences of chronic prostatitis depend on several factors:
- patient's age;
- severity of symptoms;
- current duration;
- the effectiveness of drug therapy.
The longer a man lives with chronic prostatitis, the more severe the consequences of the disease. In most cases, the urinary system is affected. With bacterial prostatitis, kidney infection is possible when urine backflows. This is due to the entry of pathogenic agents into the urethra during ejaculation.
Constant irritation of the bladder and urethra can lead to inflammation. Against the background of prostatitis, cystitis and urethritis of various nature are often diagnosed.
In chronic prostatitis, the consequences affect the psycho-emotional state of the man. Violation of potency, frequent urge to go to the toilet, discomfort in the bladder - all this leads to the development of stress. Prostatitis can be an indirect cause of neurosis and depression.
Disruption of the nervous system against the background of constant discomfort in the genitourinary organs leads to a decrease in immunity and a deterioration of all metabolic processes in the body. Thus, prostatitis provokes nervous disorders, which in turn aggravate the course of the disease, and the circle is closed.
Constant discomfort, impaired potency, inability to sleep - all this greatly affects the quality of life.
Disease Diagnostics
If prostate inflammation is suspected, a urologist or andrologist should be consulted. The following diagnostic methods are used to make a diagnosis:
- rectal palpation of the prostate;
- Ultrasound and TRUS of an organ;
- kidney ultrasound;
- prostate secretion analysis;
- PSA blood test.
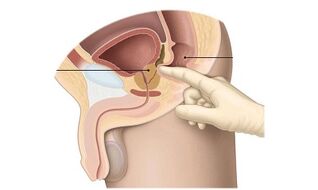
The need for further examinations is determined after rectal organ palpation. This procedure is also known as prostate massage. The doctor inserts two fingers into the rectal opening and feels the prostate. Inflammation is evidenced by a change in the structure of the organ, the heterogeneity of tissues and contours of the prostate. During the massage, the organ is stimulated and the secretion of the prostate is secreted from the urethra. It is collected for further analysis. Analysis of the prostate secretion shows:
- amount of lecithin grains;
- leukocyte and erythrocyte count;
- presence of pathogenic microorganisms;
- presence of fungal microflora.
This allows not only to determine the nature of the inflammatory process, but also to identify the pathogen in infectious prostatitis.
Ultrasound and TRUS is performed rather to exclude stones in the prostate than to diagnose prostatitis, since the method is not very informative, in contrast to the analysis of secretions.
A PSA blood test is prescribed to exclude oncopathology in the prostate gland. It also detects inflammation or prostate adenoma. How to treat chronic prostatitis depends on the test results and the type of inflammation.
Treatment features
The treatment regimen for chronic prostatitis is a combination of medication, physiotherapy and folk methods. Treatment is complemented by a change in lifestyle - adjusting the menu, giving up bad habits, regular sports and sex life.
It is important to understand that for chronic prostatitis, treatment will take at least six months. In addition to medications for relieving inflammation, men are prescribed long-term rehabilitation therapy, which is necessary to normalize the function of the prostate gland.
Medication
How to cure chronic prostatitis depends on the form of the disease. Medication for chronic prostatitis includes:
- antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs;
- rectal suppositories to normalize trophism;
- immunostimulants and general health-improving agents.
For the treatment of chronic prostatitis in men, antibiotics are used, but only if it is an infectious inflammation of the prostate. How to treat infectious prostatitis in men depends on the pathogen and the success of the previous therapeutic course. In acute bacterial inflammation, macrolide antibiotics are prescribed in most cases. They effectively suppress the activity of pathogenic agents and are distinguished by a wide spectrum of action. In case of non-compliance with the treatment regimen or improper selection of drugs, the microorganisms that caused the inflammation quickly develop resistance to macrolides, which largely causes the transition of the disease to a chronic form.
Fluoroquinolones are effective antibacterial drugs for prostatitis caused by microorganisms. They have a pronounced anti-inflammatory activity against a wide range of pathogenic microorganisms.
Despite the fact that fluoroquinolones do not have natural analogs, which is the reason for the lack of resistance of pathogenic microorganisms to the action of the drug, it is necessary to carefully follow the treatment regimen selected by the doctor. Otherwise, the drug will be ineffective and antibiotic therapy will have to be repeated.

Antibacterial drugs and tablets are not used to treat chronic non-infectious prostatitis. With congestive prostatitis, inflammation is caused not by microbes, but by a violation of trophism, therefore, it is inappropriate to use antibiotics for treatment. They use anti-inflammatory drugs instead. They are applied in short courses to reduce inflammation and swelling. The drugs are prescribed in suppositories or injections. Treatment takes one week on average, the drug is administered rectally at night or intramuscularly once a day. With severe inflammation, it is possible to use the drug twice during the day.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are not antibiotics. Tablets are successfully used to relieve the inflammatory process with non-infectious or congestive prostatitis. On average, doctors prescribe two pills daily for 5 days, and then transfer the patient to therapy with phytopreparations that improve prostate trophism.
In case of severe urination disorders, treatment is supplemented with drugs of the alpha-blocker group. These medications relax the bladder, reducing muscle tone, thereby allowing urine to flow normally. Medicines in this group are taken one tablet a day in short courses, treatment with alpha-blockers rarely exceeds one week.
After the inflammation has subsided, congestive (cognitive) and infectious prostatitis is treated with drugs that normalize the trophism of the prostate gland. Medicines contribute to:
- reduce inflammation;
- pain relief;
- normalization of urination;
- increase in potency.
For chronic prostatitis, these drugs are used for at least two weeks. They come in the form of rectal suppositories. The recommended dosage is one candle daily at night.
Propolis suppositories are recommended to restore local immunity. They relieve inflammation, improve blood circulation and outflow of prostate secretions, and also significantly increase immunity, preventing an exacerbation of prostatitis. Medicines come in the form of small suppositories that are injected into the rectum at night.
Additionally, your doctor may recommend ichthyol suppositories. They relieve inflammation and reduce swelling of the prostate gland.
Preparations based on echinacea extract are recommended as a general tonic for prostatitis. They strengthen the immune system and prevent the development of exacerbations of prostatitis. With the appearance of neuroses and insomnia against the background of prostatitis, the doctor may recommend sedatives.
Physiotherapy for chronic prostatitis
The causes of chronic prostatitis lie in poor circulation in the pelvic organs. To accelerate the recovery and restoration of trophism of the prostate, physiotherapy methods are widely used:
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- shock wave therapy;
- acupuncture.
Of the non-traditional methods, acupuncture (acupuncture) and leech therapy (hirudotherapy) are distinguished.
There are many methods of home physiotherapy. The most popular are special devices. They create alternating magnetic fields that have a positive effect on metabolic processes, eliminating congestion in the pelvic organs.
Darsonvalization can also be used at home. This is a microcurrent effect that improves metabolic processes. You can buy devices for home treatment at any medical equipment store, but it is recommended that you consult with your doctor first.
Prostate massage is used to treat congestive prostatitis. It is performed by a specialist in a medical facility. Stimulation of the organ allows you to get rid of edema and discomfort, and also relieves stagnant prostate secretion. The course of treatment consists of 10-15 procedures.
Folk remedies
Whether chronic prostatitis is treated depends on the range of therapeutic measures taken. Traditional medicine will help to complement the drug treatment.

Home-made suppositories are used to relieve inflammation in the prostate. To prepare candles, you will need 200 g of any fatty base, 40 ml of propolis extract. The base is melted in a water bath, propolis is slowly poured into it, stirring constantly. When the product acquires a uniform color, it is poured onto cling film and packed in the form of a sausage. The mass should be refrigerated for an hour to cool. When the product has cooled down, it is divided with a knife into equal torpedo-shaped pieces, approximately 5 cm long and 2 cm in diameter. These candles should be stored individually wrapped in the refrigerator. The recommended dosage is one suppository into the rectal opening before bedtime. The duration of treatment is 2-3 weeks.
You can also make candles with pumpkin seed oil and honey. The proportions are 200 g of base, 50 ml of oil and 3 tablespoons of honey. As a base, you can take beeswax, lanolin, cocoa butter. Such suppositories relieve inflammation, improve prostate function and increase immunity.
To cure chronic prostatitis at home, you can use various infusions and decoctions. One of the most effective remedies is parsley juice. It must be taken 3 large spoons daily.
Traditional medicine recommends consuming 30 g of pumpkin seeds daily. They contain many nutrients that are necessary for the normal functioning of the prostate gland.
Another effective treatment is a mixture of pumpkin seeds, walnuts, and honey. To prepare the medicine, you should take 100 peeled seeds and the same number of walnut kernels, place them in a convenient container and pour 500 ml of honey. The product is kept in the refrigerator for 4 days to infuse, and then 4 large spoons are taken daily.
Surgical Treatment
Whether chronic prostatitis can be permanently cured depends on the severity of the disease and the age of the patient. With frequent exacerbations, you have to constantly take drugs.
Surgical treatment of prostatitis in most cases is not performed. Perhaps the use of radical measures - complete removal of the prostate gland. Such an operation is carried out only if the prostate does not fulfill its functions due to chronic inflammation, and drug treatment is ineffective. Also, the removal of the prostate is practiced at the risk of developing oncology.
Interestingly, the effects of prostatitis are usually observed in old age, in men over 65. In this case, a number of difficulties arise in treatment:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- contraindications for taking medications;
- a lot of side effects.
Many men, having suffered with prostatitis for more than 10 years, insist on surgery. This is usually associated with poor drug tolerance and a large number of side effects. Doctors say that surgery is a last resort, and with the right approach, prostatitis can be cured with conservative methods.
Prevention and prognosis
Having figured out what chronic prostatitis in men is and how dangerous it is, the question immediately arises as to whether the disease can be completely cured.
Patient testimonials indicate that chronic prostatitis can be cured, but it will take a long time. The course of treatment takes on average six months or more. Urologists agree that adequate therapy, lifestyle changes and a balanced diet will help get rid of inflammation.
Most often, exacerbations and repeated episodes of inflammation after prolonged remission are encountered by those men who do not follow the doctor's recommendations, but are treated according to the advice of friends. It is important to understand that the success of treatment therapy depends on properly selected drug therapy. Lead to exacerbation or re-manifestation of signs of chronic prostatitis can:
- unsystematic medication intake;
- non-compliance with the doctor's recommendations;
- stopping treatment after the first improvement;
- bad habits;
- lack of physical activity.
Self-selection of drugs often leads to a deterioration in well-being. This is especially true in cases of infectious inflammation, when the patient independently selects antibiotics without testing.
A common mistake men make is to stop treatment when the first improvements appear. In this case, the inflammation does not go away, but only decreases for a while. With a decrease in immunity or hypothermia, the disease will again make itself felt.
Besides medication, prostatitis requires lifestyle changes. It is important to give up bad habits, normalize nutrition and start playing sports. With prostatitis, it is recommended to do yoga, exercise therapy, swimming. Any workout that involves the pelvis will benefit. Men with this condition, especially sedentary work, should do 10-minute exercises daily and do a full workout several times a week. Also, during the treatment of chronic prostatitis, it is necessary to have sex, since regular ejaculation helps to reduce prostate edema.
The success of prostatitis treatment depends on timely diagnosis, therefore, if you notice problems with urination, you should consult a urologist as soon as possible.